2nd March, 2024 (Saturday)
| CONTENT LIST | ||
| Topics | Syllabus | |
| 1 | Model Code of Conduct – Election | GS.2: Governance – Electoral Governance |
| 2 | Citizenship (Amendment) Act of 2019 | GS.2: Indian Polity – Citizenship |
| 3 | Energy Project: Sri Lanka Prefers India’s Grant Over China’s Loan | GS. 2: IR: India-Sri Lanka & China Triangle |
| 4 | GST Collection Trend | GS.3: Indian Economy – Public Finance |
| 5 | The Genome India Project | GS.3: Science & Technology |
| 6 | International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) | GS.3: Ecology & Conservation – Global Alliance |
MODEL CODE OF CONDUCT
Syllabus: GS.2: Governance: Electoral Governance
Why it’s in the News: With the Lok Sabha election approaching, the Election Commission (EC) has instructed political parties, especially star campaigners, to maintain decorum in campaigning. They are urged to refrain from using caste or communal appeals, making false statements, or resorting to divisive tactics. The directive aims to prevent indirect violations of the model code of conduct (MCC).

About the Model Code of Conduct
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) serves as a set of norms and principles designed to guide political parties and candidates during elections. It is formulated through consensus among political parties, binding them to adhere to its principles both in letter and spirit. The objectives of MCC encompass ensuring free and fair elections while preventing misuse of official machinery and curbing electoral offenses, malpractices, and corrupt activities.
- Historical Background:
- Originating from the electoral history of India, the MCC traces back to the 1960 Assembly elections in Kerala.
- It was later refined and expanded by the Election Commission of India (ECI) in response to evolving electoral challenges.
- Notably, the MCC underwent significant revisions post-1991, including measures to regulate the conduct of the ruling party to prevent unfair advantages during elections.
- Significant Provisions:
- The MCC includes provisions regulating various aspects of electoral conduct, such as:
- General conduct emphasizing the avoidance of activities fueling communal tensions.
- Regulations on campaign meetings, processions, and polling day conduct.
- Guidelines for the ruling party to prevent the misuse of official positions for electoral gain.
- Requirements for election manifestos to align with constitutional principles.
- The MCC includes provisions regulating various aspects of electoral conduct, such as:
- Issues and Controversies:
- Several challenges surround the MCC, including its lack of legal enforceability, inadequate response to new forms of electoral malpractice, and limitations in penalizing violators.
- Furthermore, the ECI faces difficulties in deregistering political parties for electoral violations, raising concerns about accountability.
- Reform Suggestions:
- To enhance MCC’s effectiveness, proposed measures include:
- Legal enforcement through integration into electoral laws.
- Utilization of existing legal frameworks for enforcement.
- Imposing bans on government-sponsored advertisements before elections.
- Integration of technology for monitoring and preventing violations.
- Granting greater independence to the Election Commission for stringent implementation.
- To enhance MCC’s effectiveness, proposed measures include:
- Conclusion
- Strengthening the MCC through legal reforms, technological advancements, and institutional autonomy is crucial for promoting transparent and equitable electoral processes in India.
- Top of Form
THE CITIZENSHIP (AMENDMENT) ACT (CAA) 2019
Syllabus: GS.2: Indian Polity – Citizenship
Why in News: Assam is set to face another round of protests against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) of 2019, with a conglomerate of 16 political parties and about 30 NGOs announcing a series of agitations.


The United Opposition Forum, led by Assam Congress president Bhupen Kumar Borah, TMC Assam president Ripun Bora, and AJP president Lurinjyoti Gogoi, gave a letter to Assam Governor Gulab Chand Kataria on February 29, 2024. In the letter, they expressed their disagreement with the Citizenship Amendment Act at the Raj Bhavan in Guwahati. | Photo Credits: API / The Hindu
About the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) 2019
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) of 2019 aims to amend the definition of illegal immigrant for specific religious communities from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh, offering them a fast track to Indian citizenship.
- This excludes Muslims and includes Hindus, Sikhs, Parsis, Buddhists, Jains, and Christians who have lived in India without documentation.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- The Act applies to individuals forced to seek refuge in India due to religious persecution. The cut-off date for eligibility is December 31, 2014.
- However, it excludes regions under the Constitution’s sixth schedule and states with an inner-line permit regime.
- Implementation Status:
- Despite being passed, the Act has faced delays in implementation due to the absence of notified rules. The government has sought extensions for framing these rules.
- Reasons for Delay:
- Opposition to the CAA, particularly in states like Assam and Tripura, has been a significant hurdle.
- Concerns have been raised over its potential impact on demographics and its perceived violation of the 1985 Assam Accord.
- Additionally, protests spread across the nation, and legal challenges have been mounted in the Supreme Court, citing violations of constitutional principles.
- Counterclaims:
- The government argues that the Act addresses specific issues in neighboring countries and is not intended as a broad solution to global persecution. It emphasizes the necessity of a reasonable classification based on religious discrimination in those countries.
- Rules and Implementation:
- While rules for implementation are now in place, the online portal is ready for applicants.
- The process will be entirely online, with no requirement for documents from applicants.
- Requests from those who applied after 2014 will be converted according to the new rules.
Conclusion
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) continues to stir controversy and protests, particularly in Assam. Despite delays, the government is pushing forward with implementation, emphasizing its necessity and addressing concerns raised by opponents.
ENERGY PROJECT: SRI LANKA PREFERS INDIA’S GRANT OVER CHINA’S LOAN
Syllabus: GS.2: IR – India – Sri Lanka & China Triangle Relations
Why it’s in the News: India secures $11 million grant to implement hybrid renewable energy project in three islands off Sri Lanka’s Jaffna peninsula, addressing energy needs with solar and wind power. This move follows objections to a Chinese energy project, signaling India’s strategic involvement in Sri Lanka’s energy sector amidst regional competition.


Sri Lanka’s Balancing Act between China, India, and New Energy Initiatives
- Sri Lanka’s economic dynamics witness a new chapter as it navigates between China and India while embracing renewable energy initiatives.
- Recent developments underscore the shifting economic alliances and the strategic importance of energy projects in Sri Lanka’s economic narrative.
- Economic Dimensions:
- Renewable Energy Initiatives:
- India’s $11-million grant for the Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems in Jaffna peninsula marks a significant milestone in addressing energy needs.
- The project, integrating solar, wind, and battery power, reflects a strategic collaboration between Sri Lanka and India to enhance energy sustainability.
- Renewable Energy Initiatives:
- India-Sri Lanka Economic Relations:
- The implementation of the hybrid power project signifies India’s continued investment in Sri Lanka’s energy sector, complementing existing projects in the region.
- India’s proactive approach, offering grants instead of loans, highlights its strategic interests and concerns over Chinese influence.
- China’s Response:
- China’s reaction to India-backed projects underscores the competition for influence in Sri Lanka’s energy landscape.
- The suspension of Chinese-backed projects and the subsequent engagement with India reflect Sri Lanka’s strategic calculations amidst geopolitical rivalries.
- Challenges and Balance:
- Geopolitical Dynamics: Sri Lanka’s delicate balancing act between China and India extends to new energy initiatives, reflecting broader geopolitical considerations.
- Economic Implications: The strategic alignment with India in energy projects may have repercussions on Sri Lanka’s economic ties with China, necessitating careful navigation.
- Conclusion:
- Sri Lanka’s economic narrative evolves as it embraces renewable energy initiatives amidst geopolitical rivalries.
- The collaboration with India in energy projects underscores the nuanced interplay between economic interests and strategic considerations.
- As Sri Lanka navigates between China and India, strategic partnerships in energy hold the key to shaping its economic future.Top of Form
GST COLLECTION TREND
Syllabus: GS.3: Indian Economy – Public Finance
Why it’s in the News: India’s gross revenues from the Goods and Services Tax (GST) grew at a three-month high pace of 12.54% in February to cross ₹1.68 lakh crore, marking the fourth-highest monthly collections from the tax.
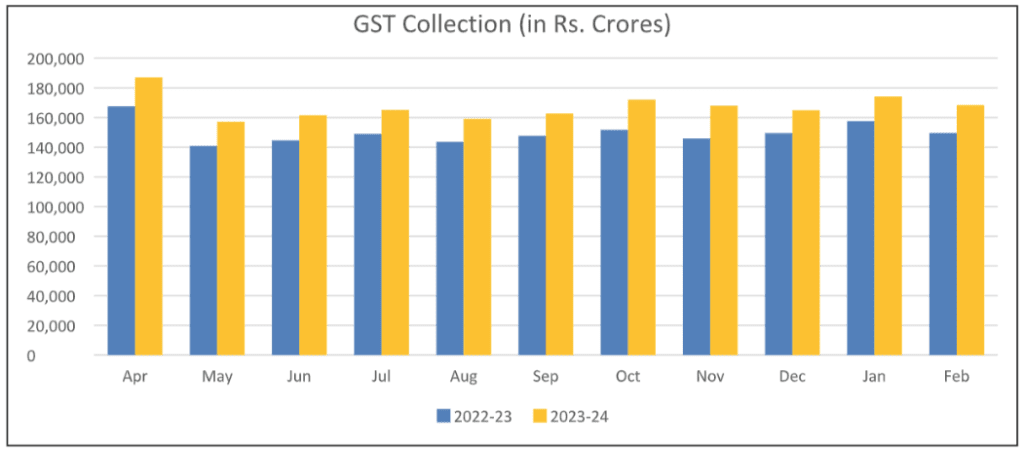

About the GST Collection Trends
- India’s gross revenues from the Goods and Services Tax (GST) surged by 12.54% in February, reaching ₹1.68 lakh crore, marking the fourth-highest monthly collections.
- This growth, the third highest in the fiscal year 2023-24, propelled the total collections for the year to ₹18.4 lakh crore, representing an 11.7% increase from the previous year.
- Factors Driving Increased GST Revenue
- Economic Revival: With the acceleration of the vaccination drive and easing of restrictions, there’s been a notable improvement in economic activity and consumption demand.
- Enhanced Compliance: Government initiatives such as e-invoicing, e-way bills, and stringent actions against tax evasion have contributed to improved compliance, reducing revenue leakages.
- Significance of Increased GST Revenue
- Economic Resilience: The uptick in GST revenue underscores the resilience of the Indian economy in recovering from the pandemic’s impact.
- Fiscal Support: It offers crucial fiscal space for both the Centre and the States to meet expenditure commitments and aid economic recovery.
- GST System Stability: The consistent revenue growth enhances the credibility and stability of the GST system, a cornerstone of India’s tax reforms.
- Areas for Improvement
- Simplification of GST Rates: Rationalizing the multiple rates and slabs would mitigate confusion, compliance costs, and litigation.
- Harmonization of Laws: Streamlining GST laws and procedures across the Centre and States would enhance consistency and ease of compliance.
- Expansion of Tax Base: Bringing more sectors under the GST ambit could broaden the tax base and improve revenue collections.
- Strengthening the GST Council: Ensuring effective functioning and decision-making within the GST Council would foster cooperation and resolution of critical issues.
- Conclusion
- While the increase in GST revenue signals positive economic trends, it should not breed complacency.
- Continuous vigilance, innovation, and reforms are imperative to transform GST into a system that benefits all stakeholders and sustains India’s economic growth trajectory.
GENOME SEQUENCING & THE GENOME INDIA PROJECT
Syllabus: GS. 3: Science & Technology
Why it’s in the News: The completion of the Genome India Project funded and coordinated by the Department of Biotechnology, which has sequenced 10,000 Indian genomes to create a reference Indian human genome. While acknowledging that 10,000 individuals may not fully represent India’s diverse population, it emphasizes the significance of this achievement as a vital template for further insights, particularly in combating diseases.

About Genome Sequencing
- The Human Genome:
- The human genome comprises the complete set of DNA found in the nucleus of every cell in the human body.
- It contains the genetic information essential for an organism’s development and function.
- The DNA is composed of adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), forming approximately 3.05 billion base pairs.
- Genome Sequencing:
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the precise order of base pairs within an organism’s DNA.
- This procedure unveils the unique genetic makeup of individuals.
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a widely used method due to its speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
- Applications of Genome Sequencing
- Rare Disorder Evaluation
- Genome sequencing plays a crucial role in evaluating rare disorders and predispositions to diseases, including cancers.
- Numerous disorders stem from single gene mutations, such as cystic fibrosis and thalassemia.
- Prenatal Screening Tool
- It serves as a tool for prenatal screening, enabling the identification of genetic disorders or anomalies in fetuses.
- Technologies like CRISPR, relying on sequencing, hold promise for repairing disease-causing mutations.
- Public Health
- Genome sequencing has significant implications for public health, aiding in the surveillance and analysis of viral genomes.
- Notably, during the Ebola and COVID-19 outbreaks, sequencing facilitated the understanding of transmission pathways, vaccine development, and diagnostic tool creation.
- Population-Level Utilization
- By analyzing genomic profiles across populations, advanced analytics and AI can enhance our understanding of disease causation and potential treatments.
- This approach promises tailored healthcare solutions based on genetic diversity.
- Rare Disorder Evaluation
- The Human Genome Project (HGP)
- Initiated in 1990, the Human Genome Project aimed to map and sequences the entire human genome.
- The project culminated in 2023 with the release of the complete human genome, with a minimal error margin.
- This milestone paved the way for personalized genomic analysis, aiding in identifying genetic variations and their implications for health.
- About Genome India Project:
- The Genome India Project, sanctioned by the Department of Biotechnology, aims to create a comprehensive genetic database of the Indian population.
- By sequencing over 10,000 genomes from diverse Indian regions, the project seeks to establish a reference genome and explore unique genetic variants.
- Significance
- This initiative will unravel genetic variations specific to Indian populations, aiding in personalized medicine and disease management.
- Given India’s vast population diversity, understanding genetic predispositions is crucial for tackling prevalent diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and cancer.
- Database for a Diverse Population
- With over 1.3 billion people and numerous endogamous population groups, India hosts a rich genetic diversity.
- Disease-causing mutations may be amplified within specific groups, necessitating a comprehensive genetic database tailored to India’s unique demographics.
Conclusion
- Genome sequencing revolutionizes healthcare by offering insights into individual genetic profiles and population-wide genetic variations.
- Projects like the Genome India initiative are pivotal for leveraging genetic data to enhance healthcare outcomes and address prevalent health challenges effectively.
INTERNATIONAL BIG CAT ALLIANCE (IBCA)
Syllabus: GS.3: Ecology & Conservation – Global Alliance
Why it’s in the News: The Union Environment Ministry aims to establish an International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), modeled after the International Solar Alliance. This initiative, approved by the Cabinet, seeks to promote global efforts for big cat conservation.


About International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- The Union Cabinet’s recent approval for the establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) marks a significant milestone in global conservation efforts.
- With a substantial budgetary support of Rs.150 crore allocated for a five-year period from 2023-24 to 2027-28, the IBCA aims to address the urgent need for coordinated action to protect and preserve the world’s big cat species.
- Background:
- Launched in 2023 by India, the IBCA commemorates the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger, which was initiated in 1973.
- Its primary objective is to facilitate cooperation among nations and agencies to arrest the decline in big cat populations and reverse this alarming trend.
- Objectives:
- To ensure cooperation for the conservation of seven big cat species, including lions, tigers, leopards, cheetahs, snow leopards, jaguars, and pumas.
- To establish a central repository for knowledge sharing, capacity building, networking, advocacy, financing, and supporting research in big cat conservation.
- Partnership and Administration:
- The IBCA encompasses 96 big cat range countries, along with interested non-range countries, conservation partners, and scientific organizations dedicated to big cat conservation.
- Its administration includes an assembly of members, a standing committee, and a secretariat based in India.
- The framework of agreement, or statute, has been drafted largely on the pattern of the successful International Solar Alliance established in 2015.
- About Big Cats:
- Big cats, typically members of the Felidae family, encompass species such as lions, tigers, leopards, cheetahs, snow leopards, jaguars, and pumas. While the term often applies to members of the Panthera genus, it also includes other large felids such as the puma and cheetah.
- Big Cats in India:
- The Indian subcontinent boasts a rich history of being home to several big cat species, including the Bengal tiger, Asiatic lion, Indian leopard, Indian/Asiatic cheetah, and snow leopard.
- Notably, five out of the seven recognized big cat species are found in India, with ongoing conservation efforts to protect these majestic creatures.
- Conclusion:
- The establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance represents a crucial step forward in global conservation efforts.
- By fostering collaboration among nations, organizations, and stakeholders, the IBCA aims to safeguard the future of big cat species worldwide.
- With its ambitious objectives and comprehensive framework, the alliance holds promise in addressing the pressing challenges facing these iconic creatures and ensuring their survival for generations to come.


