22nd February, 2024 (Thursday)
| CONTENT LIST | ||
| Topics | Syllabus | |
| 1 | India-Middle East Economic Corridor | GS. 2: IR: India & West |
| 2 | Process of Inclusion in the ST List | GS.2: Social Justice – Vulnerable Section |
| 3 | CE-20 cryogenic engine | GS. 3: Space Science |
| 4 | Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) | GS.3: Agriculture Sector |
| 5 | US-India Defense Accelerator Ecosystem (INDUS-X) | GS.2: IR: India & US Ties |
| 6 | Financial Stability and Development Council | GS.2: Governance: Corporate Governance |
| 7 | Digital Public Infrastructure | GS. 2: Digital Governance |
INDIA-MIDDLE EAST-EUROPE ECONOMIC CORRIDOR (IMEC)
Syllabus: GS. 2: IR – India & West
Why it’s in the News: Greek Prime Minister Mitsotakis reaffirmed commitment to India-Middle East Economic Corridor despite Gaza conflict’s disruption. He emphasized its potential for connectivity, trade, and cooperation, proposing Greece as a gateway to Europe.
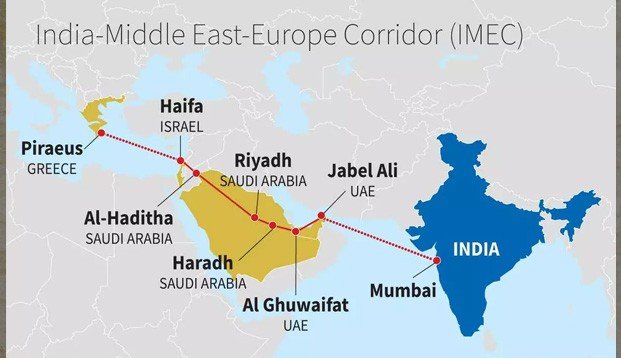
About India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) aims to bolster economic growth by enhancing connectivity and integration across Asia, the Arabian Gulf, and Europe. Key focuses include bolstering manufacturing, ensuring food security, and optimizing supply chains.
- Components of IMEC
- Eastern Corridor: Connecting India to the Arabian Gulf via rail, ship-to-rail networks, and road transport routes.
- Northern Corridor: Linking the Gulf region to Europe through similar transportation infrastructure.
- Expansion potential includes energy resource transportation through pipelines and data transmission via an optical fiber network.
- Significance of IMEC
- Alternative to BRI: Offers an alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative, avoiding perceived debt traps.
- Deepening Arabian Peninsula Engagement: Strengthens ties between India and the Arabian Peninsula.
- Indo-US Collaboration in the Middle East: Demonstrates potential collaboration beyond the Indo-Pacific.
- Stability in the Middle East: Aims to reduce tensions and promote intra-regional connectivity.
- Integration of Europe: Highlights Europe’s involvement in regional infrastructure development.
- Engagement with Africa: Proposes collaboration on a Trans-African corridor.
- Bypassing Pakistan: Overcomes Pakistan’s veto on India’s overland connectivity to the West.
- Ports Involved in IMEC
- Ports range from India (Mundra, Kandla, Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust) to the Middle East (Fujairah, Jebel Ali, Abu Dhabi, Dammam, Ras Al Khair), Israel (Haifa), and Europe (Piraeus, Messina, Marseille).
- Challenges Associated with IMEC
- Challenges include logistical coordination, financial investment, and potential disruption of existing trade routes.
- The Way Forward for IMEC
- To realize IMEC:
- Technical standardization and planning for smooth operation.
- Managing geopolitical concerns by accommodating participating nations’ interests.
- Reinforcing environmental responsibility to minimize negative impacts.
- Maintaining security apparatus in unstable regions along the route.
- IMEC promises to enhance regional connectivity, but careful planning and cooperation are essential for its successful implementation.
- To realize IMEC:
PROCESS OF INCLUSION IN THE ST LIST
Syllabus: GS. 2: Social Justice: Scheduled Tribes – Vulnerable Section
Why it’s in the News: Manipur HC withdraws directive for Meiteis’ ST inclusion, amidst conflict. Controversial paragraph removed from order triggering ethnic tensions. Tribal bodies appeal against order, pending review.
Procedure and Criteria for Inclusion in Scheduled Tribes List
- The process for inclusion begins with proposals originating from State or Union Territory governments.
- The Union Tribal Affairs Ministry forwards these to the Office of the Registrar General of India (ORGI).
- Following ORGI’s approval, the proposal goes to the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, adhering to criteria established by the Lokur Committee in 1965.
- Ultimately, Cabinet approval and Presidential notification enact the amendment.
Benefits of Inclusion / Constitutional Safeguards
- Inclusion in the Scheduled Tribes list entails constitutional safeguards such as reservations in education (Article 15(4)), posts and services (Article 16(4), 16(4A), 16(4B)), seats in Panchayats (Article 243D), and Lok Sabha representation (Article 330).
Criticism and Government Response
- Critics argue that the inclusion process, labeled as “obsolete” and “cumbersome,” hampers timely recognition of deserving communities.
- Despite government insistence on adequacy, a task force highlighted flaws, including the exclusion of numerous communities.
Supreme Court Intervention
- In response to concerns, the Supreme Court seeks to establish precise parameters for identifying Scheduled Tribe status, addressing the need for a comprehensive framework to determine eligibility.
- The Manipur HC’s withdrawal of the Meiteis’ ST inclusion directive amidst conflict highlights the complexity of the process, prompting scrutiny and Supreme Court intervention for clearer criteria.
- Top of Form
CE-20 CRYOGENIC ENGINE
Syllabus: GS.3: Science & Technology
Why in News: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has accomplished a major milestone in the human rating of its CE20 cryogenic engine that powers the cryogenic stage of the human-rated LVM3 launch vehicle for Gaganyaan missions with completion of the final round of ground qualification tests.

About the Cryogenic Technology
- Cryogenic technology, characterized by ultra-low temperature applications, has propelled India’s space exploration endeavors, notably through the development of the CE-20 cryogenic engine.
- This engine, along with recent milestones achieved in human-rating standards, underscores India’s growing prowess in space technology.
Evolution of Cryogenic Technology in India
- India’s journey in mastering cryogenic technology reflects remarkable milestones:
- Formal approval of the Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) project in 1994 marked the inception.
- The development of CE-20 in 2014 represented a significant leap in India’s cryogenic capabilities. Recent endeavors, including human-rating tests and acceptance tests for the Gaganyaan program, demonstrate ISRO’s commitment to excellence and safety standards.
- Future Prospects:
- Integrated Manufacturing Facilities Initiatives like the Integrated Cryogenic Engine Manufacturing Facility (ICMF) by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) underscore India’s commitment to self-reliance: Centralizing manufacturing processes for cryogenic and semi-cryogenic engines, the ICMF streamlines production and enhances efficiency.
About the CE-20 Cryogenic Engine
- The CE-20 cryogenic engine, crafted by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) under ISRO, represents a pinnacle of Indian engineering:
- Designed for the Cryogenic Upper Stage of the LVM3 launch vehicle.
- Incorporates innovative gas-generator cycle technology.
- Ranks among the world’s most powerful upper-stage cryogenic engines, boasting a vacuum thrust of 186.36 kN.
- Significance of Cryogenic Technology for India
- India’s advancements in cryogenic technology hold profound implications for its space missions:
- Independence in Space Launches: With indigenous cryogenic engines, India no longer relies on other nations for launching heavier payloads into space.
- Enhanced Payload Capacity: Cryogenic engines offer higher specific impulse, translating to increased payload capacity and mission efficiency.
- Human-Rated CE20 Engine: ISRO’s accomplishment in human-rating the CE20 cryogenic engine signifies a pivotal step towards crewed space missions, ensuring safety and reliability in transporting humans.
- Chandrayaan-3 Mission: Leveraging Cryogenic Power The upcoming Chandrayaan-3 mission exemplifies India’s utilization of cryogenic technology:
- A successor to Chandrayaan-2, Chandrayaan-3 aims to demonstrate India’s capability in lunar surface exploration.
- Powered by the CE-20 cryogenic engine, the mission comprises major modules including the Propulsion, Lander, and Rover.
- Conclusion
- The CE-20 cryogenic engine and India’s advancements in cryogenic technology symbolize a remarkable journey towards self-sufficiency in space exploration.
- With innovations driving progress and human-rating standards achieved, India is poised to achieve new milestones, shaping the future of crewed space missions and reaffirming its status as a global space power.
Top of Form
FAIR AND REMUNERATIVE PRICE (FRP)
Syllabus: GS.3: Agriculture Sector: Government Interventions
Why it’s in the News: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved a ₹340/quintal Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) for sugarcane in the 2024-25 seasons, with a 10.25% sugar recovery rate. This is an 8% increase from the current season’s FRP. The new rate will be effective from October 1, 2024.

About Fair and remunerative price (FRP):
- Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) denotes the minimum price at which sugar mills are obligated to purchase sugarcane from farmers.
- This crucial price point is determined by the Union government through the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- The regulatory framework governing FRP is established under the Sugarcane (Control) Order of 1966.
- Factors Influencing FRP Determination:
- The methodology for determining FRP is comprehensive, taking into account various factors such as the cost of production, prevailing demand-supply dynamics, domestic and international market prices, and inter-crop price parity.
- This meticulous approach ensures a fair assessment of the value of sugarcane, providing a reliable income source for farmers.
- Key Benefits of FRP:
- One of the primary advantages of FRP is its assurance of reasonable margins to farmers, irrespective of the profitability of sugar mills.
- This mechanism safeguards farmers’ interests and sustains their livelihoods, contributing to the overall welfare of the agricultural community.
- Moreover, the uniform applicability of FRP nationwide ensures equitable treatment for farmers across regions.
- State-Level Interventions:
- In addition to the FRP, certain states such as Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu announce a State Advised Price (SAP), which typically exceeds the FRP.
- These state-level interventions further augment farmers’ income, reflecting localized agricultural realities and cost considerations.
- Conclusion:
- The recent approval of an enhanced FRP for sugarcane exemplifies the government’s proactive measures to support agricultural stakeholders.
- By ensuring fair compensation for farmers’ produce, the FRP mechanism plays a pivotal role in enhancing agricultural sustainability and rural prosperity.
- Moving forward, continued collaboration between policymakers, agricultural experts, and farmers is essential to further refine and optimize FRP policies, thereby fostering a robust agricultural ecosystem.
US-INDIA DEFENSE ACCELERATOR ECOSYSTEM (INDUS-X)
Syllabus: GS. 3: Indian Economy: Types of Inflation
Why it’s in the News: The Defence Secretary emphasized the significance of initiatives like INDUS-X in fostering collaboration, innovation, and interoperability between India and the U.S. to address common threats, particularly regarding China, highlighting intelligence sharing and technology development showcased in the summit.

About INDUS-X
- The ‘INDUS-X’ summit, launched in June 2023, stands as a significant joint endeavor between India and the US, aimed at advancing bilateral defense cooperation and fostering strategic technology partnerships.
- Aim:
- To enhance defense innovation and technology collaboration between the two nations.
- Objectives:
- Advancing Strategic Cooperation: Expand strategic technology partnerships and defense industrial cooperation.
- Bridging Innovation Gaps: Establish a defense innovation bridge covering joint challenges, academia engagement, industry-startup connect, and investment in defense projects.
- Focus Areas:
- Foster horizontal cooperation between governments, academia, and laboratories, and vertical partnerships between established defense primes and startups or SMEs.
- Increase collaboration between startups and prime contractors for critical defense assets.
- Support India’s goal of achieving $5 billion in defense exports by 2025.
- Contribute to a more stable and secure Indo-Pacific region.
- Key Participants:
- India’s Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX), U.S. Department of Defense, U.S.-India Business Council (USIBC), U.S. Chamber of Commerce, and Society of Indian Defence Manufacturers (SIDM).
- About Innovations for Defense Excellence (iDEX):
- Launched in 2018 by the Ministry of Defence, Government of India, iDEX aims to foster innovation and technology development in the defense and aerospace sectors.
- Significance:
- Funding: Provides grants and funds to support R&D efforts and facilitate the creation of functional prototypes.
- Inclusive Growth: Creates a culture of engagement with innovative startups and encourages co-creation for defense and aerospace sectors.
- Engagement with the Industrial sector: Focuses on engaging industries, including MSMEs and startups, to deliver advanced solutions.
- Collaboration: Works through programs like the Defense India Startup Challenge (DISC), involving problem statements from Armed Forces, DPSUs, and OFB.
- Implementation of Program: Implemented by the Defense Innovation Organization (DIO), a not-for-profit company formed under the Companies Act 2013, the iDEX framework aims to make India self-reliant in defense matters by fostering innovation and technology development in the defense and aerospace sector.
Top of Form
FINANCIAL STABILITY AND DEVELOPMENT COUNCIL (FSDC)
Syllabus: GS. 2: Corporate Governance
Why it’s in the News: Fresh measures to curb unauthorised online lending apps’ operations could be on the anvil, following deliberations on the issue at the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) chaired by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.

About Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC)
- The Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) is a pivotal forum established by the Government of India in December 2010 to address crucial matters concerning financial stability and sectoral development.
- Despite lacking statutory authority and a separate allocation of funds, FSDC plays a critical role in coordinating efforts across various regulatory bodies and government departments.
- Objectives
- The primary objectives of FSDC encompass:
- Enhancing Financial Stability: FSDC aims to fortify and institutionalize mechanisms that uphold financial stability within the Indian economy.
- Inter-regulatory Coordination: It endeavors to improve coordination among different financial sector regulators, fostering a cohesive regulatory environment.
- Promoting Sectoral Development: FSDC is committed to advancing the development of the financial sector through strategic initiatives and policy interventions.
- The primary objectives of FSDC encompass:
- Composition
- The composition of FSDC includes:
- Chairperson: The Union Finance Minister of India leads the council, providing direction and oversight.
- Members: Key members consist of heads of financial sector regulators such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA), Forward Markets Commission (FMC), along with senior officials from relevant government departments including Finance Secretary, Secretary of Economic Affairs, Secretary of Financial Services, and Chief Economic Adviser.
- Expert Participation: FSDC has the flexibility to invite domain experts to its meetings, enriching discussions and decision-making processes.
- The composition of FSDC includes:
- Functions
- Macroeconomic Supervision: It monitors the macroprudential supervision of the economy, including overseeing the operations of large financial conglomerates to mitigate systemic risks.
- Inter-regulatory Coordination: Addressing coordination challenges among regulatory bodies to ensure a harmonized regulatory framework.
- Financial Inclusion and Literacy: FSDC emphasizes the importance of financial literacy and inclusion, aiming to extend financial services to marginalized sections of society.
DIGITAL PUBLIC INFRASTRUCTURE (DPI)
Syllabus: GS. 2: Digital Governance
Why it’s in the News: Digital Public Infrastructures (DPIs) are projected to propel India towards a $1 trillion digital economy by 2030, aiding its transition to an $8 trillion economy, as per a report by Nasscom-Arthur D. Little.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): Revolutionizing Public Services
- DPI encompasses foundational digital platforms facilitating public service delivery across sectors such as identification, payments, healthcare, education, and governance.
- Positioned as an intermediary layer in the digital ecosystem, DPI bridges the connectivity and hardware layer with various digital applications.

India’s Leadership in DPI
- India has led DPI development with initiatives like India Stack, featuring Jan-Dhan Accounts, Aadhaar, and Mobile numbers (JAM Trinity).
- Jan-Dhan Accounts ensure financial inclusion, Aadhaar provides unique digital identity to over 1.4 billion Indians, and BHIM-UPI revolutionizes digital transactions.
Significance of DPI
- Enhances efficiency and transparency in public service delivery, as seen with Aadhaar enabling access to government schemes.
- Fosters digital inclusion, empowerment, innovation, and aligns with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Challenges in DPI Development
- Vulnerabilities to cyber-attacks, regulatory gaps, governance issues, funding and infrastructure gaps, and digital inequality.
Steps for Strengthening DPI
- Implement comprehensive cybersecurity measures, invest in scalable and resilient technologies, promote business agility, ensure operational excellence, encourage innovation, establish a robust regulatory framework, build governance capacity, sustain investment, and promote digital literacy.
- Conclusion
- DPI is a transformative force in modernizing public service delivery, with India leading through innovative initiatives. Addressing challenges and strategic implementation can further strengthen DPI’s impact, fostering inclusive development and sustainable progress.


